Understanding How the Effects of Drugs on the Brain Cause Addiction
Regardless of the type of drug involved, addictive drugs all exert certain effects that increase the likelihood of ongoing drug use. Also known as psychoactive agents, these drugs are able to cross the blood-brain barrier, which gives them easy access to the brain’s workings.
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, drug addiction creates a diseased state inside the brain that’s complex in nature. By the time addiction sets in, the effects of drugs on the brain override any intention or will on the user’s part.
The effects of drugs on the brain impact key chemical processes that eventually alter and/or destroy the brain’s structures over time. In the process, a person’s motivations and overall ability to learn revolve around the effects of drugs on the brain.
Psychoactive Drug Effects
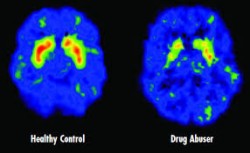
Drugs can cause significant changes in the brain.
Psychoactive drugs can be categorized according to the types of effects they have on the brain:
- Stimulants stimulate or speed up brain and central nervous system (CNS) functions
- Depressants slow down brain and CNS functions
- Hallucinogens disrupt overall brain function
- Sedatives also slow down brain and CNS functions
These varied effects of drugs on the brain correspond with the types of brain chemical processes targeted by any one drug.
In effect, the psychoactive effects of drugs on the brain cause groups of brain cells to secrete abnormally high levels of neurotransmitter chemicals. These chemical secretions account for the drug’s “high” effects as well as any medicinal effects a drug may have.
With continued drug use, chemical processes grow dependent on a drug’s effects and become unable to function normally in the absence of the drug. This cycle sets a person up for physical dependency and eventual psychological dependency as the effects of drugs on the brain continue to warp the brain’s chemical processes.
The Brain’s Reward System
The brain’s reward system regulates learning processes and determines what motivates a person to act. According to the University of Utah Health Sciences, dopamine, a neurotransmitter chemical, is one of the chemicals most affected by the effects of drugs on the brain. Dopamine also plays a key role within the brain’s reward system circuitry.
Every time a person ingests a psychoactive drug, high levels of dopamine flood the brain’s reward system. Each time this happens, the reward system associates the act of using drugs as a positive stimulus. In the process, a person “learns” that taking drugs is good, which in turn motivates ongoing drug-using behaviors.
Deteriorating Brain Structures
While the “highs” experienced from drugs can easily fuel a person’s ongoing drug use, deteriorating brain cell structures drive continued drug use on another level. Weakening cell structures require increasingly larger doses of drugs to produce the same desired effects, so a person’s tolerance level will continue to rise as long as he or she keeps using.
These interactions set a vicious cycle in motion. With continued drug use, the effects of drugs on the brain cause widespread deterioration that can become permanent. This cumulative effect accounts for why recovering addicts remain at risk for relapse for years after their last drug use.
