Opiates and the Brain – How Addiction Happens
Opiate addiction develops out of a series of changes that take place inside the brain. Over time, these changes alter the brain’s overall structures and chemical processes. As these alterations take shape, a vicious cycle of opiates and the brain ensues for as long as a person continues to use.
According to the U. S. National Library of Medicine, alterations in brain function become actual brain abnormalities that stem from the ongoing effects of opiates and the brain. As opiates and opiate-derived drugs hold certain chemical similarities to the brain’s own natural chemicals, the brain is naturally susceptible to the effects of ongoing opiate use.
Certain key stages mark the process of addiction as opiates and the brain become more and more intricately entwined. Increasing tolerance levels, physical dependence and withdrawal all work together to drive the compulsive, drug-seeking behaviors that define addiction.
Opiate Effects
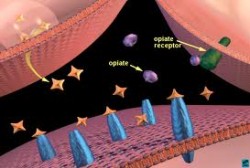
The way opiates function in the brain can cause tolerance, dependence, and addiction.
Opiates originate from the opium poppy seed plant. The opium plant contains natural pain-relieving compounds. Likewise, the brain secretes its own natural pain relieving chemicals, also known as endorphins.
Not surprisingly, the opium plant’s compounds and the brain’s endorphin chemicals bear a strong resemblance to one another. This similarity in chemical structure accounts for why opiates and the brain become a lethal combination when a person abuses this type of drug. When ingested, opiates slow down the body’s central nervous system functions in the same way the brain’s natural endorphin chemicals do.
Tolerance Level Effects
Opiates and the brain naturally take to one another, which accounts for how quickly an addiction can develop. While most people who abuse opiates do so to experience feelings of euphoria and calm, the chemical processes taking place in the brain take on a life of their own with continued drug use.
Brain cell receptor sites normally secrete endorphins on an as needed basis, whereas repeated drug use weakens and eventually warps receptor site functions. As brain cells grow weaker, larger doses of the drug are needed to produce the same desired “high” experience. In effect, opiates and the brain form an increasingly stronger bond the longer a person uses.
Physical Dependence & Withdrawal
With opiates and the brain, physical dependence and withdrawal effects tend to go hand-in-hand. Physical dependence increases as the brain’s tolerance for opiates rises. As the brain grows more dependent on opiate effects, withdrawal effects not only occur more often, but also grow in intensity.
The brain also has a self-regulating mechanism that automatically adjusts endorphin secretion amounts whenever too much or too little is being produced. As a result, it takes even larger doses of the drug to trigger endorphin secretions.
Brain Reward System Effects
The brain’s reward system plays a central role in regulating learning and motivation. Every time a person experiences a “high,” this part of the brain interprets the experience as a positive stimulus. With repeated use, this positive reinforcement mechanism grows. The vicious cycle between opiates and the brain picks up momentum at this point.
In essence, the brain’s reward system creates a memory or record of:
- Where a person used drugs
- With whom
- The circumstances involved
- Anticipation or feelings prior to drug use
In the process, drug use becomes a learned behavior. Once a person reaches this stage, both a physical and psychological dependency have developed, and addiction is in full force.